Achieve Full Language Fluency with the Deep Integration of Languages into Your Daily Life
Achieving full language fluency is certainly not easy. The internet is filled with all sorts of advice on how to do it. And that's on top of all those shiny lists of language learning tools. No wonder, after all, these are extremely important elements in the whole process. However, in a whirlwind of all kinds of language learning discussions, it's easy to lose sight of one thing - the criterion of utility.
The utility criterion tells us one very simple thing - we should preferentially use things that are directly applicable in our lives.
It doesn't matter how much time you spend going through your textbooks. If the language is not part of your life, the textbook will most often be thrown in the corner at the first sign of a life/time crisis.
It is not difficult to imagine that you are going on vacation for 2 weeks and completely neglect your studies because YOLO, and "let's party dude!". Or suddenly you get sick and you feel so weak that you lack the strength to lift a book.
Sure, you can blame this state of affairs on your lack of willpower or the adverse conjunction of the planets, but the fact is that your contact with language has been neglected because it is not a part of your life!
Full language fluency - languages as a versatile tool
Perhaps the entire system of education is to blame. We are used to thinking that language is yet another school subject. Or thinking that learning a language is drudgery and that "I will cram a couple more words and then I am finally free and will do something interesting."
We forget that language is a tool. And not just any! We're not talking about a rusty knife with a bent handle.
We're talking about a cool Swiss army knife!
There are many ways to integrate languages into your daily life to guarantee that you will achieve full fluency.
Remember that the deeper the integration, the greater the chance that you will learn the language not only fluently but also quickly.
Foreign languages as a tool for entertainment
Broadly understood entertainment is certainly one of the easiest changes you can make. There are so many ways to relax after all! What's more, nobody has to force us to do it. I am yet to hear a mom yelling at her son, "Stop learning, you dweeb. Watch something for once. Oh! I have failed as a parent!".
Here are a few "entertainment" categories that you should include in your daily plan:
Remember that no activity is a waste of time if it is done in a foreign language.
1) Full language fluency - Music

Music is not only a great tool to improve your listening comprehension, but it can also help you to remember words better.
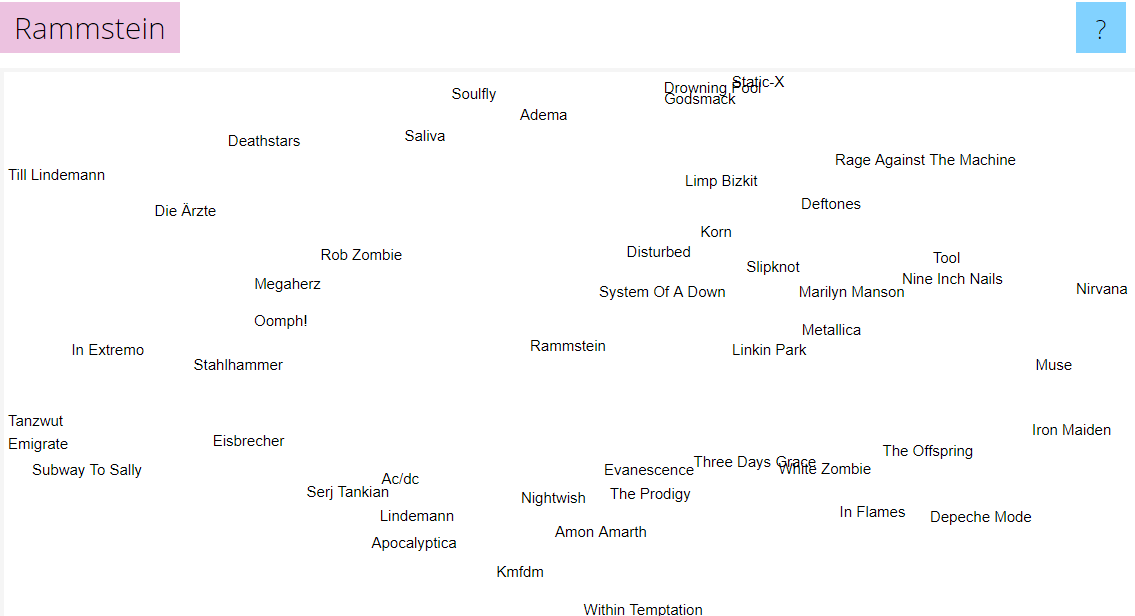
If you don't know what to listen to in the language of your choice, I highly recommend the Music Map website. It allows you to quickly find a lot of exciting artists based on your current musical tastes.
In other words - enter the artist's name and enjoy the sweet view of dozens of other artists.
Here is an example for Rammstein:



2) Full language fluency - watching movies / series
Films, and in particular TV series, are one of the pleasures you don't need to convince anyone of. Often, no more than a few days is enough to get an incurable condition called "one more episode-itis".
Here is a list of some interesting sites where you can watch TV series or movies in the original language or dubbed. Feel free to add your suggestions in the comment section.
You can find more resources in my Language Links Database.
I recommend Netflix in particular. You can change a default language of TV series and movies there as well as enable subtitles.
And all this without worrying that the link on the page does not work or that you will see for the 10th time in one day "Do you want to meet singles in your area?". It is one of the best language investments I've made over many years.
3) Full language fluency - exploring interests
Like most people, you are probably quirky. You have your own world, and your own interests to which you can effortlessly devote lots of time. Why not use it to get one step close to achieving full language fluency?
It doesn't matter if you are interested in reading thyme dregs or a 50-meter chinchilla throw. I guarantee you that a little googling is enough to find forums or websites of people who share your passion.
Here are some examples of interesting sites:
4) Full language fluency - gossip magazines
I will say it again - nothing is a waste of time if it is done in foreign languages! The next time your husband catches you reading about Brad Pitt's iron buttocks, just shout shrilly "I'm learning! Do not disturb!" Or do it in German to fluster him. That works better than a pepper spray.
I feel dirty writing this, but here are some recommendations:
5) Full language fluency - Computer games
If you are hellbent on keeping the last link connecting your childhood with the cold and cruel world of adults alive, I recommend taking up computer games. Especially those that are rich in various dialogues.
The best site where you can find computer games in many languages is Steam.
Foreign language as a tool for professional development




Photo by Dylan Gillis on Unsplash
The modern world is not a welcoming place. If you have any hopes of becoming a force to be reckoned with, you need to develop and sharpen your skills continually. Just a moment of inattention is enough to get mangled by the competition, who will then proceed to graciously stomp over your carcass. Terrible. I know.
I recommend finding your preferred sources of specialized information in languages of your choice. This is the easiest way always to be one step ahead of most people in your industry.
Warning - the initial shock
It is worth mentioning that deep integration of a foreign language into life is not all butterflies and rainbows. Initially, you may feel strong resistance from the brain. This pink, slimy bastard will try to talk you out of trying to surround yourself with a foreign language, "John, don't learn Korean! What will neighbors say?".
You should be ready for it. It will pass with time. However, it remains an open question how much time will be needed for this.
If you already have some experience with intensive language learning, you probably won't need much time to get used to new experiences. If you're inexperienced, accept that you'll need up to a few weeks.
Achieving Full language fluency - Summary
Often the main difference between a person who has mastered a language and the one who has given up is the extent to which they have made the language part of their lives.
Each additional activity performed in a given language anchors it even deeper.
Such integration will make your learning fully resistant to the turmoils of life. The border between "cramming" and normal life will begin to blur, and eventually it will disappear.
You will always know when this moment will come, as it is truly unforgettable. It reveals itself in the following question: "Did I read / hear it in a foreign language or in my native tongue?"
Done reading? Time to learn!
Reading articles online is a great way to expand your knowledge. However, the sad thing is that after barely 1 day, we tend to forget most of the things we have read.
I am on the mission to change it. I have created over 12 flashcards that you can download to truly learn information from this article. It’s enough to download ANKI, and you’re good to go. This way, you will be able to speed up your learning in a more impactful way.